Adverbs of Frequency, Even and Also
How often do you speak English? Every day? Very often? Sometimes? Hardly ever? Never?? Well if you do an online course with the Central School of English, you’ll be speaking like a native before you know it!
Yes, you’ve guessed it…in this blog we are going to look at adverbs of frequency!
How often do you....?
Adverbs of frequency help to answer the question ‘How often…?’.
For example, someone might ask you:
How often do you go to the gym?
Some possible answers to this question are:
I usually go to the gym three times a week.
I sometimes go to the gym at weekends.
I hardly ever go to the gym.
I never go to the gym.
The box below shows common adverbs of frequency and the percentage of frequency they represent.
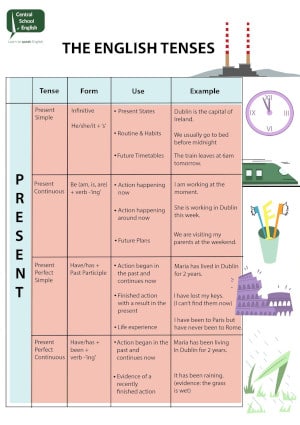
Adverbs of frequency
100% Always
90% Usually
80% Normally, generally
70% Often, frequently
50% Sometimes
30% Occasionally
10% Rarely, seldom
5% Hardly ever
0% Never
The percentages (%) in the box above are a guideline. Adverbs of frequency should not always be taken literally. For example, I might say:
I always drink coffee. I never drink tea.
This does not mean that I drink coffee 24 hours a day. That would be quite difficult and unhealthy! It probably means that I drink a lot of coffee but no tea.
Position of adverbs of frequency
A good rule of thumb to help us remember the position of adverbs of frequency is:
Adverbs of frequency come after the first auxiliary verb.
Here’s an example of a sentence with two auxiliary verbs:
I have never been skiing in the Alps.
In this sentence there are two auxiliary verbs – have and been. The adverb of frequency ‘never’ comes after the first auxiliary verb ‘have’.
However it is not very common to have two auxiliary verbs in a sentence. This means that the adverb of frequency simply comes after the auxiliary verb. This happens in tenses that have an auxiliary verb such as the perfect tenses (auxiliary: to have) and the continuous tenses (auxiliary: to be).
Here’s a few examples of sentences with one auxiliary verb and an adverb of frequency:
She has often worked on Sundays.
I had rarely seen such a beautiful landscape.
John is always borrowing my computer.
We have never been to Egypt.
Adverbs of frequency with the present simple tense
The most common use of adverbs of frequency is when we use the present tense to talk about our routines and habits. In the present tense there is no auxiliary verb in a positive sentence. When there is no auxiliary verb we generally put the adverb of frequency between the subject and the verb.
Here are some examples of adverbs of frequency with the present simple tense:
Kate always gets up early.
They hardly ever go to the cinema.
Peter sometimes goes swimming after work.
My cat generally sleeps all day.
The sun always rises.
You rarely eat fish and chips.
Adverbs of frequency in negative sentences
We sometimes use adverbs of frequency in negative sentences. In this case the adverb generally goes after the word not.
Here are some examples of adverbs of frequency used in negative sentences:
Kate doesn’t always get up early.
They don’t often go to the cinema.
Peter doesn’t usually go swimming after work.
My cat doesn’t generally sleep at night.
The moon doesn’t always shine.
Even and Also
The words even and also are both adverbs.
Even
We use the adverb even to refer to something surprising, unexpected, unusual or extreme.
When even is used in a whole clause or sentence, we also usually put it in the same position as adverbs of frequency – between the subject and the main verb, after a modal verb or the first auxiliary verb.
For example, we might say:
Susan hates all animals. She even hates kittens.
Mark won’t go out. He won’t even go to work.
The children can speak four languages. They can even speak Japanese.
Also
We use also to add a new piece of information, without the suggestion that it is surprising.
When also is used in a whole clause or sentence, we also usually put it in the same position as adverbs of frequency – between the subject and the main verb, after a modal verb or the first auxiliary verb.
For example, we might say:
Children study history in school. They also study science.
The man ordered 3 desserts. He also left a very small tip for the waiter.
The Central School has classes Monday to Friday. It also has classes on Saturday.
Test Yourself
Vocabulary
A native: A person who has grown up and lives in a specific country and is a native speaker of the language of that country
Example: She has only been in Dublin for a few months but she already speaks English like a native.
Before you know it:Very quickly
Example: If you practice the guitar every day, before you know it you’ll be playing your favourite songs!
To take something literally: To interpret every word in a sentence to be completely true
Example: Some people take the Bible literally.
Idioms
Rule of thumb: A guideline that is generally based on experience rather than exact calculations
Example: As a rule of thumb, you should drink two litres of water every day.
Thank you for reading our post. You’ll find more English grammar tips elsewhere on our site and if you’d like information on our English courses in Dublin, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Learn to SPEAK English
Join a live online English tutor to get help with your English.
Individual and group classes with our expert teachers.